Causes of Hyperpigmentation and How to Prevent It
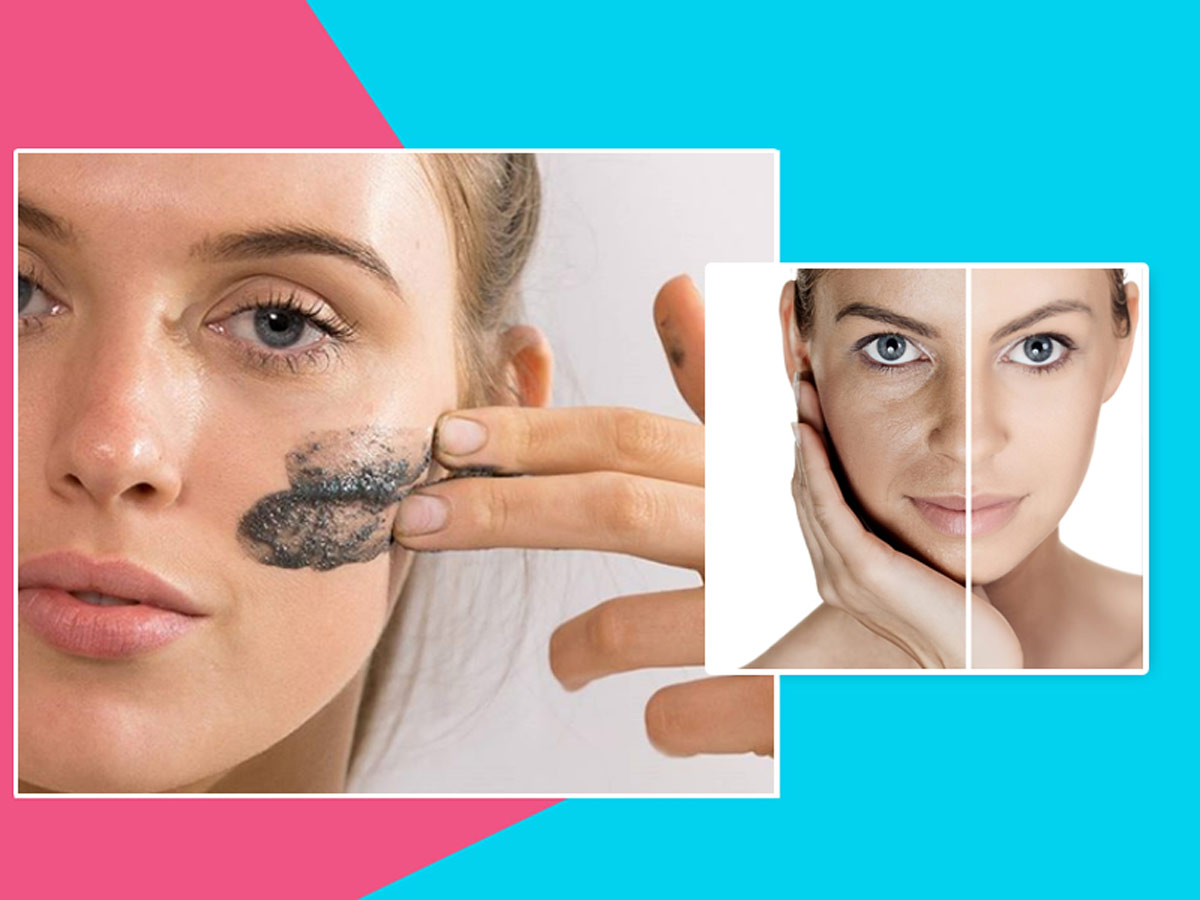

Hyperpigmentation is a common skin condition characterized by patches or areas of the skin that become darker than the surrounding skin tone. It occurs due to an overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin, hair, and eye color. While hyperpigmentation is generally harmless, it can be a source of concern for many individuals, affecting their self-esteem. In this blog, we will explore the causes of hyperpigmentation and provide some effective preventive measures to maintain healthy, even-toned skin.
Sun Exposure
One of the leading causes of hyperpigmentation is prolonged and unprotected exposure to the sun’s harmful ultraviolet (UV) rays. UV radiation triggers melanocytes to produce more melanin as a defense mechanism against the sun’s damage. Consequently, areas exposed to the sun, such as the face, neck, hands, and arms, are more susceptible to developing dark spots or age spots.
Prevention tip: Regularly apply broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF, wear protective clothing, and limit sun exposure during peak hours to shield your skin from UV rays.
Hormonal Changes
Fluctuations in hormones can also contribute to hyperpigmentation. Pregnant women often experience melasma, a type of hyperpigmentation commonly known as the “mask of pregnancy.” Hormonal birth control methods and hormonal therapies may also trigger dark spots in some individuals.
Prevention tip: If you are pregnant or using hormonal treatments, consult with your healthcare provider for personalized skincare advice and appropriate preventive measures.
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH)
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation occurs after an injury, inflammation, or skin trauma, such as acne, cuts, burns, or skin infections. When the skin heals, it may produce excess melanin, leading to dark spots.


Prevention tip: To minimize the risk of PIH, avoid picking or squeezing acne, and treat inflammatory skin conditions promptly under the guidance of a dermatologist.
Skin Irritants and Allergens
Certain cosmetic products or skin care ingredients can cause skin irritation and trigger hyperpigmentation in sensitive individuals. Allergic reactions may also lead to dark patches.
Prevention tip: Choose gentle, non-comedogenic, and hypoallergenic skincare products. Perform a patch test before trying new products to check for any adverse reactions.
Aging
As we age, the skin’s natural repair processes may slow down, and accumulated sun damage over the years can manifest as hyperpigmentation, commonly referred to as age spots or liver spots.
Prevention tip: Regularly use anti-aging products containing ingredients like retinoids and antioxidants to boost skin rejuvenation and minimize the appearance of age-related hyperpigmentation.
Genetic Predisposition
Some individuals may be genetically predisposed to developing hyperpigmentation, making them more susceptible to dark spots and uneven skin tone.
Prevention tip: While you cannot change your genetics, adopting a consistent skincare routine and adhering to preventive measures can help manage hyperpigmentation effectively.

Established in 2001,
Under the supervision of
Senior Dermatologist
and Cosmetologist
Dr. Padmavathi Surapaneni
Contact
-
6-3-347/22b/1/1, Saibaba temple lane,
Panjagutta, Hyderabad-500082. - Book an Appointment
- +91 9848367000
- +91 40 66827999
- +91 40 66666399
- +91 40 23356070/80
Recent Posts
Copyright © 2023 Pragna Skin Care and Laser Clinic. All rights reserved